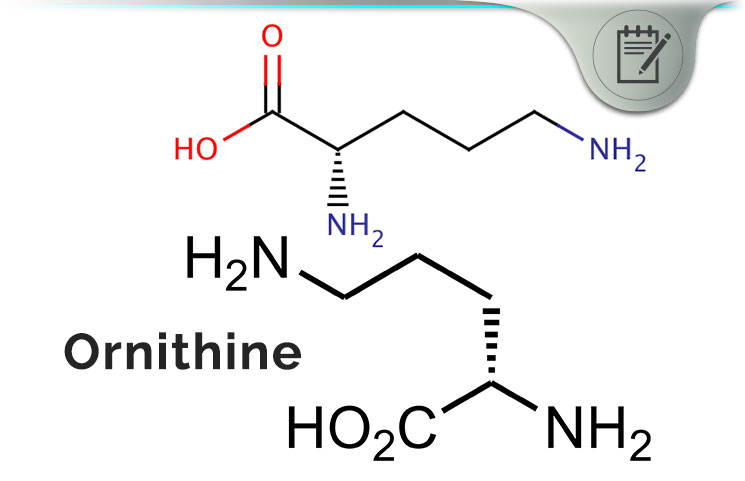
Ornithine is a non-proteinogenic amino acid that is naturally involved in the urea cycle. It is one of three amino acids involved in the cycle, the others being L-Arginine and L-Citrulline. Ornithine being a non-proteinogenic amino acid means it is not found as a genetically coded amino acid in any organism, so it cannot be used to create proteins. It does play a crucial role in the urea cycle.
When the cells of the body break down proteins, they produce a compound known as ammonia. Ornithine is then binded with carboamyl-phosphate, a compound that requires ammonia production in the cells. L-ornithine is then converted into L-Citrulline, releasing urea as the by-product of the reaction. The process is known as the ornithine cycle.
Deficiency of ornithine in the body could result in very severe consequences in the body. It results in excessive levels of ammonia in the liver, which is catastrophic as ammonia is toxic unless excreted.
It leads to such conditions as hepatic encephalopathy and another known as ornithine transcarbamylase deficiency. This is a rare hereditary condition affecting 1 in 80,000 people. It is characterized by excessive accumulation of ammonia in the blood. It causes severe fatigue and could even result in seizures.
Patients with the these disorders are given ornithine supplementary drugs. Ornithine in this context is therefore the artificially synthesized version of the ornithine found in the body. It is sold as a drug to supplement those with deficiency, and has other uses as well.
Benefits Of Ornithine
Ornithine is given as a supplement to people suffering from hepatic encephalopathy. From research and studies conducted on various patients, it has been shown to decrease the levels of personal fatigue in the victims, indicating a reduction in the levels of ammonia in the blood.
Ornithine is a compound that is converted to arginine at the liver. Arginine is a chemical that is an intermediary in the formation of nitric oxide. Nitric oxide is crucial to the body in terms of energy supply to the tissues. Nitric oxide is a compound that is essential in the dilation of blood vessels when they are required to dilate in order to supply more blood to tissues requiring it.
More blood to the tissues means more glucose is taken to the tissues. This results in an increased amount of energy to the said tissues. So, intake of ornithine by people not deficient in the same is thought to increase their energy levels through the process. So it is recommended for people doing cardiovascular exercise, and for for people who suffer from fatigue as a supplement to food.
Ornithine has also been known to help people suffering from hangovers after taking alcohol. This is due to the fact that intake of a lot of alcohol results in highly increased levels of ammonia in the body. The dilated levels of ammonia are thought to be responsible for the symptoms of hangovers, such as severe headaches and fatigue. The ornithine has to be taken before the intake of alcohol for it to have any effect in the body.
There was also old research into the benefits of ornithine in boosting output and increasing lean mass in weightlifters and bodybuilders. However, the research is unvisited and unrevised, and the practical relevance of the study is little to none.
In light of this, ornithine has also been seen to increase the growth hormone. It has effects similar to those of arginine. However, the effects of ornithine are generally short lived. Because the growth hormone functions by increasing lean mass and decreasing the fat content of the body, these things are more dependent on the daily lifestyle of the person as opposed to short bursts and increments of ornithine in the body.
Recent animal tests on the effects of ornithine in the body have proven very successful. The amino acid was injected into the animals and showed increased wound healing in the animals. This is because it boosted the production of collagen.
Collagen is crucial in the formation of connective tissue in the body. The amino acid also, when introduced in the animals, showed a decrease in the anxiety levels of the subjects as well.
In a publication in the November 2011 issue of “Nutrition and Neuroscience,” the amino acid crossed the blood brain barrier, thus effecting the change in the animal’s behavior. These tests were positive, but are yet to be subjected to human subjects.
Basically, the most important and verified use of ornithine to humans right now is the decrease of ammonia levels in the blood. This decreases fatigue and thus can be vital when performing prolonged exercise. It increases exercise duration by up to 45 minutes. This is partly due to the increased levels of blood in the tissues.

Possible Side Effects
It is important to note that ornithine is not vastly tested and approved. In this way, its side effects to pregnant women and breast feeding mothers are not very clear. To stay on the safe side, pregnant women and breast feeding mothers are advised to consume it.
One may also be allergic to the other products in the medication itself. It is best to consult your doctor before purchasing the supplements.
Top Ornithine Products
The following are the top ten most recommended ornithine products:
- Nutricost L-Ornithine: It Has Been Reported To Increase The Body’s Ability To Build Muscle.
- Xpi-Hgf 1: This Product Contains Pure L-Ornithine And Has Been Said To Reduce Fat Content In The Body Dramatically And Boost The Lean Mass Of The Muscles.
- Snc Igf-1 Protocol.
- Musclephram Arnold Iron Pump
- Universal Nutrition Gh Max
- Xpi Amino Powder
- High Energy Labs High Complete
- Muscle Elements Amino Flow
- Universal Nutrition Gh Stack
- Muscle Core Humovox
Ornithine Review Summary
Ornithine is a good supplement for people with fatigue. It is key for people doing cardiovascular exercises as it boost the amount of time you can do exercises. It can boost the duration by up to 45 minutes. However, it is not thoroughly tested for other uses.